Radiation Oncology
Radiation Oncology
Radiation oncology is a medical specialty that focuses on the use of radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer and other diseases. Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, involves the use of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells or prevent them from growing and dividing. Radiation oncologists are physicians who specialize in the field of radiation oncology. They work closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including medical oncologists, surgical oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, and others, to develop and deliver comprehensive cancer treatment plans.
The role of a radiation oncologist includes:
Treatment planning: Radiation oncologists collaborate with other specialists to determine the most appropriate use of radiation therapy for each patient. They review medical history, diagnostic imaging, pathology reports, and other relevant information to develop an individualized treatment plan. This plan takes into account the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health.
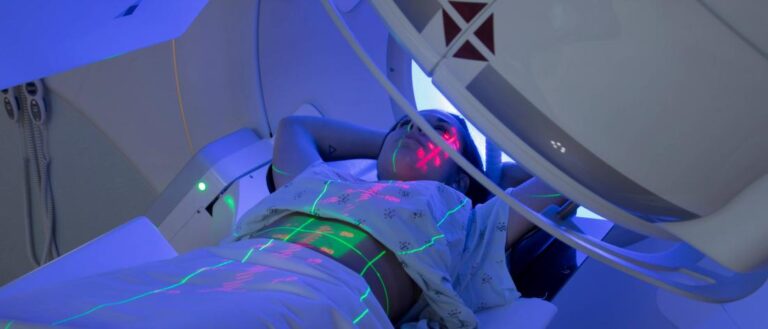
Radiation therapy administration: Radiation oncologists oversee the delivery of radiation therapy to patients. They determine the appropriate dose, schedule, and technique for treatment. Radiation therapy can be delivered using external beam radiation (where a machine directs radiation towards the tumor from outside the body) or internal radiation (where a radioactive source is placed inside or near the tumor). The radiation oncologist ensures that the treatment is precisely targeted to the tumor while minimizing radiation exposure to healthy tissues.
Treatment monitoring and adjustment: Throughout the course of radiation therapy, radiation oncologists closely monitor patients to assess treatment response and manage any side effects that may arise. They may conduct regular check-ups, perform imaging scans, and modify treatment plans if necessary to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Palliative radiation therapy: Radiation oncologists may also provide palliative radiation therapy to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients with advanced cancer. Palliative radiation aims to shrink tumors, relieve pain, control bleeding, or address other cancer-related symptoms.
Long-term follow-up: Radiation oncologists provide long-term follow-up care to monitor the patient’s progress after radiation therapy. They conduct regular check-ups, assess treatment outcomes, and manage any late effects or complications that may arise from radiation treatment.
Radiation oncology is a rapidly evolving field with ongoing advancements in radiation technology, treatment planning, and delivery techniques. Radiation oncologists stay abreast of these advancements to ensure the safe and effective use of radiation therapy in cancer treatment. They work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive and personalized care to patients.

